This article explains reverse DNS, when to use it, and how to set it up for your account.
What is reverse DNS, and how does it work?
IP addresses are resolved to domain names via reverse DNS lookups (also known as reverse DNS resolution or rDNS). Regular DNS resolution (also known as forwarding DNS lookups) takes a domain name as input and returns the IP address associated with it. Forward DNS lookups utilize A records to get an IP address for a domain name, whereas reverse DNS lookups use PTR records to find the domain name associated with an IP address.
External e-mail servers often need PTR records for sending domains as an anti-spam precaution. If a transmitting domain does not have a PTR record, the message is rejected by the e-mail server, which typically includes an error message in the SMTP headers stating that reverse DNS is not set.
Details for the systems :
Before PTR records operate correctly, they need authoritative DNS nameservers. Trace the Start Of Authority (SOA) record of your server’s primary IP address to locate the authoritative DNS nameservers. Run the following command to do this:
dig +nssearch 0.168.192.in-addr.arpaAdd the reverse DNS zone
NOTE:-
1. This interface does not currently support IPv6.
2. If your hosting provider delegates a byte boundary to you that is greater than 25, separate the network range and byte boundary with a dash (–) character. Do not use a forward slash (/) character.
For example,
128-24.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa
1. Log into “WHM as a root account”
2. Search for the “DNS Function”
3. Click on “Add a DNS Zone”
4. In the IPv4 Address text box, type your Server’s IP address.
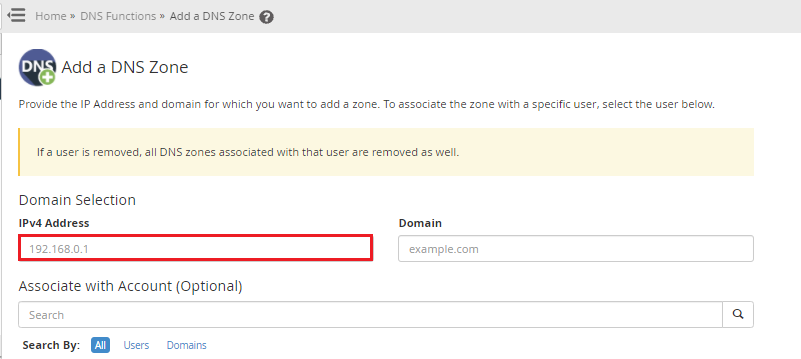
5. In the Domain text box, type the name of the reverse DNS zone.
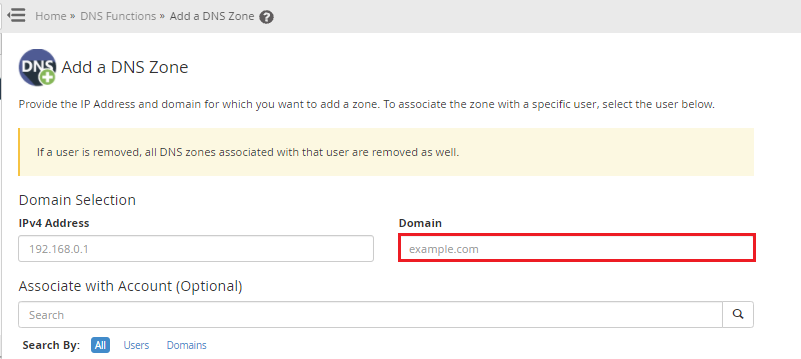
6. For an IPv4 address, create a reverse DNS zone name. Follow these steps to accomplish this:
Remove the IP address’s last octet.
Reverse the remaining octets’ order.
Append .in-addr.arpa to the end of the octets.
A complete reverse DNS zone name for an IPv4 address will resemble the following example:
128/24.0.168.192.in-addr.arpaWe hope that you now have a good understanding of how to set reverse DNS. If you continue to have problems with the protocol outlined above, please contact the Webhosting UK for constructive assistance 24×7 days a week.
